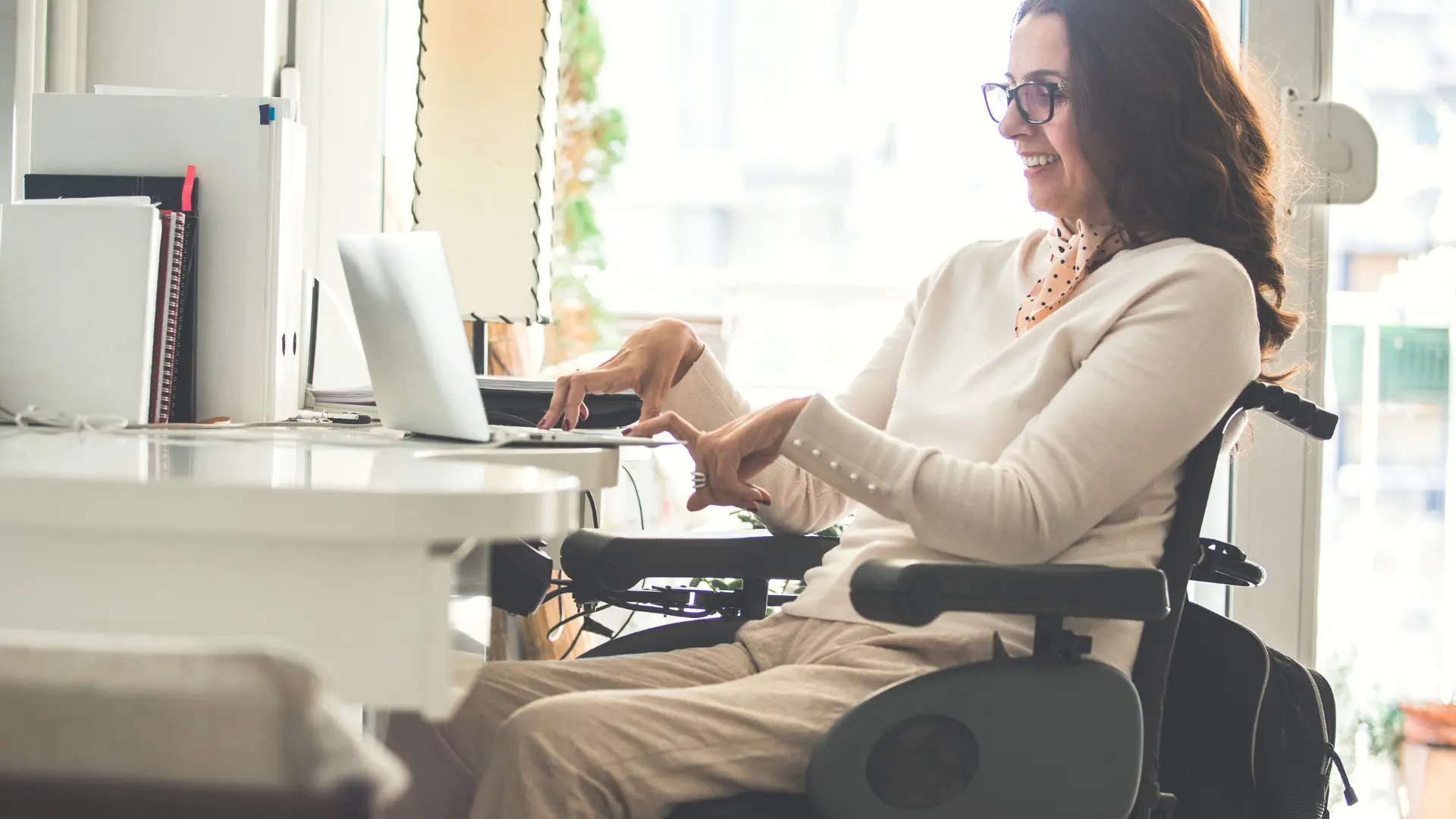
Telemedicine can significantly improve access to healthcare for individuals with disabilities who may face challenges in physically accessing traditional healthcare facilities. People with mobility issues, for instance, may find it difficult to travel to medical appointments, but telemedicine allows them to consult healthcare professionals remotely from the comfort of their homes.
Through telemedicine, PwD can experience greater convenience. They can schedule appointments at times that suit them best, without having to navigate transportation or deal with the logistics of attending in-person appointments.
For individuals with certain disabilities, such as chronic conditions or mobility impairments, telemedicine solutions can include remote monitoring devices that allow healthcare providers to track their health status and intervene promptly if necessary. This proactive approach to healthcare management can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Challenges arise with the readiness users are asked to have to operate such ICT demanding technologies. Considering that even minor disabilities constrain most PwD to perform basic activities, telecare and telemedicine, irrespective of their usefulness, may seem an unrealistic goal.
Basic healthcare systems and facilities lack basic accessibility features (digital and physical), turning more healthcare solutions out of reach for most PwD. Turning effective telecare solutions into accessible ones could be a serious step for giving access to PwD to reach basic care services that currently cannot. Starting with a digitally accessible Medical Folder, or conducting teleconsultation services with specifically made sessions for people with visual and hearing impairments, like the one customly developed in CarePOI, is a starting point for supporting the so-far-uncovered care needs.
Hara Pylarinou.